
Now that School is finished,
Most of you are moving to High School,
and I’m going to miss you A LOT!!!


Now that School is finished,
Most of you are moving to High School,
and I’m going to miss you A LOT!!!

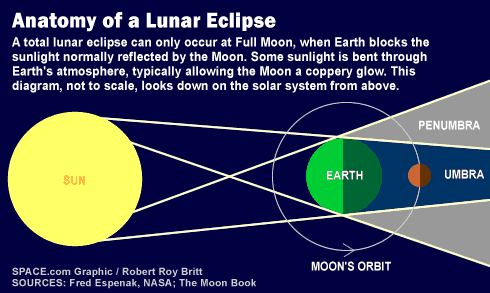
A total lunar eclipse is taking place on June 15, 2011. It is the first of two such eclipses in 2011, the second occurring on December 10, 2011. Read more
and HAVE A GREAT WEEKEND!! 
absolute monarchy: form of government where the king or queen has absolute power on all aspects of his or her subjects’ life.
architect: a person who designs buildings.
astrolabe: ancient instrument used by navigators and astronomers to determine latitude, longitude and time of day. It also determines the altitude of the Sun, planets, stars and Moon.
authoritarian monarchy: the politic system in which the kings in 15th Century have all the power.
bourgeois: the inhabitant of walled towns, formed by craftsmen, merchants…
caravel: a light sailing ship with two or three masts and lateen sails used by the Spanish and Portuguese in the 15th and 16th Centuries.
Classical culture: name given to the influence of Ancient Greek or Roman civilizations on language, philosophy, art… in the Renaissance.
clergy: the official leaders of a religious belief. colonisation: n. the act or process of establishing colonies.
compass: an instrument that is used for finding directions. It has a dial and a magnetic needle that always points to the North.
craftsman: a man who makes things skilfully with his hands.
decline: the period when something approaches an end.
Discovery: the act of discovering a place or a thing.
Golden Age: a flourishing period in arts and literature that took place in Spain during the 16th and 17th Centuries.
literature: name given to all creative writing of recognised artistic value.
Modern Age: the term used by historians to refer a period in the History from 1492 (Discovery of America) until 1789 (French Revolution).
navigation: the guidance of ships from place to place.
painter: an artist who paints.
patron: a person who supports and gives money to artists, writers or musicians.
peasant: a person who works on the land.
portolan charts: European navigation maps based on realistic descriptions of harbours and coasts.
Renaissance: means re-birth. A cultural movement that spanned roughly from the 14th Century to the 17th Century. It began in Italy and it later spread to the rest of Europe.
sculptor: a person who creates sculptures.
sextant: navigational instrument used to measure the altitude of a celestial object above the horizon and to determine its latitude and longitude.
silk: valuable/delicate cloth made from the fine treads produced by certain insect larvae.
spice: any of a variety of pungent or aromatic vegetable substances used to for seasoning food.
writer: a person who writes books, stories or articles as a job.
The Enlightenment: a philosophical and cultural movement in the eighteenth century that stressed human reasoning over blind faith and encouraged scientific thinking.

1. When does the Modern Ages begin?
2. When does the Modern Ages end?
3. What does Renaissance mean?
4. What were the people of Renaissance most interested in?
5. Who supported artists, writers or musicians during the Renaissance?
We use the Reported Speech when we want to report what someone else said before.
Direct speech | Reported speech |
"I always drink coffee". She said. | She said that she always drank coffee. |
|
|
- Although the most common verbs are say, tell and ask, we can use verbs such as explain, promise, say, tell, suggest...
- It is not neccesary to change the verb tense if the verb in the direct speech is in the present.
- that can be omited.
- When we make a sentence in Reported Speech, the verb moves a step backwards in time:
Direct speech | Reported speech |
present simple | past simple |
present continuos | past continuos |
past simple | past perfect |
present perfect | past perfect |
present perfect continuos | past perfect continuos |
future | simple conditional |
future perfect |
CAN | COULD |
MAY | MIGHT |
WILL | WOULD |
MUST | HAD TO |
keep: the strongest or central tower of a castle.
kingdom: a country, state, or territory ruled by a king or queen.
knight: a medieval gentleman-soldier, usually high-born, raised by a sovereign to privileged military status after training as a page and squire.
moat: a deep, wide defensive ditch surrounding a castle or town, typically filled with water.
mosque: a Muslim place of worship and prayer.
nobleman: man (or woman) who belongs to the aristocracy.
peasant: a member of the class constituted by small farmers and tenants, sharecroppers, and labourers on the land where they form the main labour force in agriculture.
pilgrim: a person who journeys to a sacred place for religious reasons.
reconquest: second or new acquisition by physical or moral force.
sword: a weapon with a long metal blade and a hilt with a handguard, used for thrusting or striking.
synagogue: a building where a Jewish assembly or congregation meets for religious worship and prayer.
alcazaba: a Moorish fortified building used for defence by the Arabs in Spain.
armour: the metal coverings formerly worn by knights to protect the body in battle.
bailey: the open area within a castle fortification.
castle: a large fortified building or group of buildings, typically of the medieval period.
church: a building for public, especially Christian worship.
monks: the body of people ordained for religious duties in the Christian Church.
craftsman: a worker skilled in a particular craft or manual job.
drawbridge: a bridge which is hinged at one end so that it can be raised.
feudalism: the social system in medieval Europe, in which the nobility held lands from the Crown in exchange for military service, and vassals were tenants of and protected by the nobles.
guild: a medieval association of craftsmen or merchants.


1. When do the Middle Ages begin?
2. When do the Middle Ages end?
3. What event marks the beginning of the Middle Ages?
4. What event marks the end of the Middle Ages
5. What religions coexisted in Spain in the Middle Ages?
6. How was society organized?
7. What was the job of the king?
8. What was the job of the noblemen?
9. What was the job of the knights?
10. What was the job of the clergy?
11. What was the job of the peasants?
12. What were the guilds?
13. How many kingdoms were there in Iberian Peninsula in the Middle Ages?
14. Name three differences between the Muslims and the Christians.
15. What were castles and alcazabas for?
16. What were churches, mosques, and synagogues for?

Tomorrow (21st May) we are celebrating World Day for Cultural Diversity for Dialogue and Development.
Are you aware of diverse cultures? Why not create mandalas to symbolize peace and harmony?
World Day for Cultural Diversity for Dialogue and Development: Mandalas
This is my selection of interesting websites. They are all related to the World Day for Cultural Diversity for Dialogue and Development and offer extra ideas, songs, crafts and many more resources.
Happy surfing!
United Nations – Cultural Diversity Day
UNESCO – Third International Festival of Diversity
Seguro que estos mapas te ayudan a repasar la geografía física y socioeconómica de España.

International Museum Day is celebrated on 18 May each year. The theme for 2011 is Museum and Memory.
International Museum Day was established in 1977 by the International Council of Museums (ICOM), and was first celebrated in 1978. It, and future International Museum Days, would be:
... accompanied by the opening of new museums and exhibitions, meetings with visitors, acquaintance of the public with the aims and tasks and practical activity of the International Council of Museums and its national organisations, publication of materials on this subject in the press and also by the organisation of exchange exhibitions and international forums to discuss major problems of the theory and practice of the museum profession.
12th General Assembly of ICOM, Resolution No 5, 28 May 1977
Numantia is the name of an ancient Celtiberian settlement, whose remains are located 7 km north of the city of Soria, on a hill known as Cerro de la Muela in the municipality of Garray.
Numantia is famous for its role in the Celtiberian Wars. In the year 153 BC Numantia experienced its first serious conflict with Rome. After 20 years of hostilities, in the year 133 BC the Roman Senate gave Scipio Aemilianus Africanus the task of destroying Numantia. He laid siege to the city, erecting a nine kilometre fence supported by towers, moats, impaling rods and so on. After 13 months of siege, the Numantians decided to burn the city and die free rather than live and be slaves.
Read more.
IF + SUBJECT + PAST PERFECT, SUBJECT + WOULD + HAVE + PAST PARTICIPLE
SUBJECT + WOULD + HAVE + PAST PARTICIPLE + IF + SUBJECT + PAST PERFECT
The third conditional (also called conditional type 3) is a structure used for talking about unreal situations in the past.
The first conditional and second conditionals talk about the future. With the third conditional we talk about the past. We talk about a condition in the past that did not happen. That is why there is no possibility for this condition. The third conditional is also like a dream, but with no possibility of the dream coming true.
Last week you bought a lottery ticket. But you did not win. :-(
condition result Past Perfect WOULD HAVE + Past Participle If I had won the lottery I would have bought a car.
Notice that we are thinking about an impossible past condition. You did not win the lottery. So the condition was not true, and that particular condition can never be true because it is finished. We use the past perfect tense to talk about the impossible past condition. We use WOULD HAVE + past participle to talk about the impossible past result. The important thing about the third conditional is that both the condition and result are impossible now.
Look at some more examples in the tables below:
IF condition result past perfect WOULD HAVE + past participle If I had seen Mary I would have told her. If Tara had been free yesterday I would have invited her. If they had not passed their exam their teacher would have been sad. If it had rained yesterday would you have stayed at home? If it had rained yesterday what would you have done?
result IF condition WOULD HAVE + past participle past perfect I would have told Mary if I had seen her. I would have invited Tara if she had been free yesterday. Their teacher would have been sad if they had not passed their exam. Would you have stayed at home if it had rained yesterday? What would you have done if it had rained yesterday?
Now check your knowledge with this activity found by ALBA (6ªC):
Egypt is one of the most fertile areas of Africa, and one of the most fertile of the countries around the Mediterranean Sea. Because Egypt is so fertile, people came to live in Egypt earlier than in most places, probably around 40,000 years ago. At first there were not very many people, but gradually Egypt became more crowded, so there was more need for a unified government. For a while there seem to have been two kingdoms, which we call Upper Egypt (in the south) and Lower Egypt (in the north). Around 3000 BC (5000 years ago), at the beginning of the Bronze Age, the king of Upper Egypt conquered the king of Lower Egypt and made Egypt into one kingdom, Egypt. People called the ruler of this new kingdom the Pharaoh.
Read more.
Do you want to know more and have fun learning about Ancient Egypt??
Here is my selection of websites all related to Ancient Egypt.
Happy surfing!!
Virtual tour to an Egyptian Museum